- Atomic Mass Calculation Formula
- Relative Atomic Mass Of Sodium Chloride
- Relative Atomic Mass Of Sodium Fluoride
- Atomic Mass Of Sodium Bicarbonate
- Relative Atomic Mass Of Sodium
The mass in grams of a mol of an element is equal to the atomic mass. In the case of sodium, its atomic mass is 22.99 u (this is the relative weighted average atomic mass for sodium in atomic mass units). The mass of 1 mol of sodium atoms is the atomic mass expressed in grams, or 22.99 g. Consider the balanced equation. Density is the mass of a substance that would fill 1 cm 3 at room temperature. Relative atomic mass The mass of an atom relative to that of carbon-12. This is approximately the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. Where more than one isotope exists, the value given is the abundance weighted average.
17th Jul 2019 @ 22 min read
The formula mass is often confused with the molar mass or the molecular mass, but it differs from both. As the name suggests, it has some relation with the formula of a molecule. The formula mass is a mass calculated using the formula. It is determined by adding the average atomic masses of the atoms present in a molecule.
Definition
Atomic Mass Calculation Formula
It is the sum of the average atomic masses of the atoms in the formula of a compound. Let take an example to make it clearer, the formula of anhydrous calcium sulphate is CaSO4. We can calculate the formula mass by adding the average atomic mass of each atom present in the formula of a compound.
| Element | Number of Atoms | Average Atomic Mass (u) | Subtotal (u) |
| Ca | 1 | 40.08 | 40.08 |
| S | 1 | 32.06 | 32.06 |
| O | 4 | 16.00 | 64.00 |
| Formula Mass of CaSO4 | 136.14 | ||
As you can see from the above table the formula mass of CaSO4 is 136 u. If you have noticed, this is the same way we calculate the molecular mass of a molecule. But there is some difference, which is explained later in this article.
Units
Since it is calculated from the average atomic mass, it has the same unit of the average atomic mass. It is expressed in the unified mass unit or the dalton or the atomic mass unit. The symbol for the unit is u or amu.
Relative Formula Mass
The relative formula mass (aka the formula weight) is the sum of the atomic weights (not average atomic masses) of the atoms in the formula of a compound.
It, unlike the formula mass, is a dimensionless quantity. It does not have any unit. Both the quantities have the same numerical value, they only differ in the unit. Thus, the relative formula mass of CaSO4 is 136.14, not 136.14 u.
Note: The relative atomic mass and the atomic weight are synonymous of one another. So, we can use the relative atomic mass instead of the atomic weight in the above definition.
Difference between Molecular Mass and Formula Mass
The molecular mass is the mass of a molecule. It is estimated by adding the average atomic masses of atoms present in a molecule. The molecular mass is the same as the formula mass in some cases while in others not.
To calculate the molecule mass, we need to have a discrete molecule, which is not always a case. For example, ionic compounds like sodium chloride (NaCl), magnesium oxide (MgO), iron sulphate (FeSO4) exist in large crystal lattices. They do not have any definite molecule form. In ionic compounds, there are positively-charged cations and negatively-charged anions. These ions are arranged to form various crystal structures like monoclinic, tetragonal, orthorhombic, cubic. Thus, the concept of the molecular mass itself falls. This is where the formula mass comes into play. Instead of calculating the molecular mass, which is not possible for such compounds, we calculate the formula mass.
As we can see from the above figure sodium chloride does not exist as a discrete entity. The chemical formula of sodium chlorine is NaCl, but in the above figure, one sodium ion is surrounded by six chloride ions, which does not represent its formula. Hence, the concept of the molecular formula is out of the picture.
The difference between the molecular mass and the formula mass perishes, in case of covalent compounds. In most covalent compounds, molecules exist as a discrete entity. So, the molecular mass and the formula mass are the same. Examples of covalent compounds are methane (CH4), ethanol (C2H6O), chloroform (CHCl3), glucose (C6H12O6).
Examples and Calculations
To calculate the formula mass of any compound, we only require its formula and the average atomic mass of its elements. The average atomic mass of any element can be found from the periodic table. The below mentions some examples.
Example 1: To Determined Formula Mass of Glucose
Glucose is one of the important monosaccharides and the main source of energy in all organisms. It exists in both a straight-chain as well as a ring form.
The molecular formula of glucose is C6H12O6.
The formula mass of glucose is calculated in the below table.
| Element | Number of Atoms | Average Atomic Mass (u) | Subtotal (u) |
| C | 6 | 12.01 | 72.06 |
| H | 12 | 1.01 | 12.12 |
| O | 6 | 16.00 | 96.00 |
| Formula Mass of C6H12H6 | 180.18 | ||
The formula mass of glucose is 180.18 u and its relative formula mass is 180.18.
Example 2: To Determined Formula Mass of Paracetamol
Paracetamol is also known as acetaminophen. It is widely known as a pain reliever. Other uses of paracetamol are reducing fever, headache, lower back pain, dental pain.
The molecular formula of paracetamol is C8H9NO2.
The formula mass of paracetamol is calculated in the below table.
| Element | Number of Atoms | Average Atomic Mass (u) | Subtotal (u) |
| C | 8 | 12.01 | 96.08 |
| H | 9 | 1.01 | 9.09 |
| N | 1 | 14.01 | 14.01 |
| O | 2 | 16.00 | 32.00 |
| Formula Mass of C6H12H6 | 151.18 | ||
The formula mass of paracetamol is 151.18 u and its relative formula mass is 151.18.
Example 3: To Determined Formula Mass of Sebacic Acid
Sebacic acid is a dicarboxylic acid with the molecular formula C10H18O4. It is used as a monomer in the production of nylon-610, plasticizers, hydraulic fluids etc.
The formula mass of sebacic acid is calculated in the below table.
| Element | Number of Atoms | Average Atomic Mass (u) | Subtotal (u) |
| (C) | 10 | 12.01 | 120.1 |
| (H) | 18 | 1.01 | 18.18 |
| (O) | 4 | 16.00 | 64.00 |
| Formula Mass of (C10H18O4) | 202.3 | ||
The formula mass of sebacic acid is 202.3 u and its relative formula mass is 202.3.
Example 4: To Determined Formula Mass of Sodium Chloride
Sodium chlorine, unlike in the above examples, is an ionic compound. It does not have a discrete molecule. It consists of positively-charged sodium ions surrounded by negatively-charged chloride ions. Its chemical formula is (NaCl).
| Element | Number of Atoms | Average Atomic Mass (u) | Subtotal (u) |
| Na | 1 | 22.99 | 22.99 |
| Cl | 1 | 35.45 | 35.45 |
| Formula Mass of (NaCl) | 58.44 | ||
The formula mass of sodium chloride is (58.44 u) and its relative formula mass is 58.44.
Example 5: To Determined Formula Mass of Aluminium Sulphate
Aluminium sulphate is a water-soluble chemical compound with the chemical formula Al2(SO4)3. It is used as a coagulating agent in the purification of water. Its anhydrous form consists of two aluminium ions and three sulphate groups.
The formula mass of aluminium sulphate is calculated in the below table.
| Element | Number of Atoms | Average Atomic Mass (u) | Subtotal (u) |
| Al | 2 | 26.98 | 53.96 |
| S | 3 | 32.07 | 96.21 |
| O | 12 | 16.00 | 192.0 |
| Formula Mass of Al2(SO4)3 | 342.17 | ||
The formula mass of aluminium sulphate is 342.17 u and its relative formula mass is 342.17.
Example 5: To Determined Formula Mass of Copper Sulphate Pentahydrate
Copper sulphate is an ionic salt of copper and sulphuric acid. Its most common form is copper sulphate pentahydrate having chemical formula CuSO4·5H2O. The appearance of copper sulphate hydrates is bright blue in colour.
The formula mass of copper sulphate is calculated in the below table.
| Element | Number of Atoms | Average Atomic Mass (u) | Subtotal (u) |
| Cu | 1 | 63.55 | 63.55 |
| S | 1 | 32.07 | 32.07 |
| H | 10 | 1.01 | 10.1 |
| O | 9 | 16.00 | 144.0 |
| Formula Mass of CuSO4·5H2O | 249.7 | ||
The formula mass of copper sulphate is 249.7 u and its relative formula mass is 249.7.
Associated Articles
If you appreciate our work, consider supporting us on ❤️ patreon.- 0
- cite
- response
Copy Article Cite
Whenever you see the words ‘relative’ in chemistry, it means the mass number.
Example
Relative atomic mass = find the mass number
Relative formula mass = find the mass number
Note: if you see the phrase ‘atomic mass’ on its own, it’s incorrect. It should always have the word ‘relative’ in front of it.
Note for higher tier Chemistry students
Relative atomic mass = find the (average) mass number
Relative atomic mass actually infers that the element has isotopes. To find the relative atomic mass, you will need to work out the average mass of the isotopes.
Relative atomic mass
The relative atomic mass of an element is equal to its mass number.
Examples of relative atomic mass
Mass number = 1
Atomic number = 1
Relative atomic mass of hydrogen = 1
Mass number = 12
Atomic number = 6
Relative atomic mass of carbon = 12
Relative formula mass
To work out the relative formula mass of a compound, just add up all the relative masses within its formula.
Examples of relative formula mass

Water (H2O)
Mass number = 1
Atomic number = 1
Relative atomic mass of hydrogen = 1
Mass number = 16
Atomic number = 8
Relative atomic mass of oxygen = 16
As there are 2 hydrogen atoms and 1 oxygen atom in a water molecule, the calculation is (2x1) + 16 = 18.
Therefore, the relative formula mass of H2O is 18.
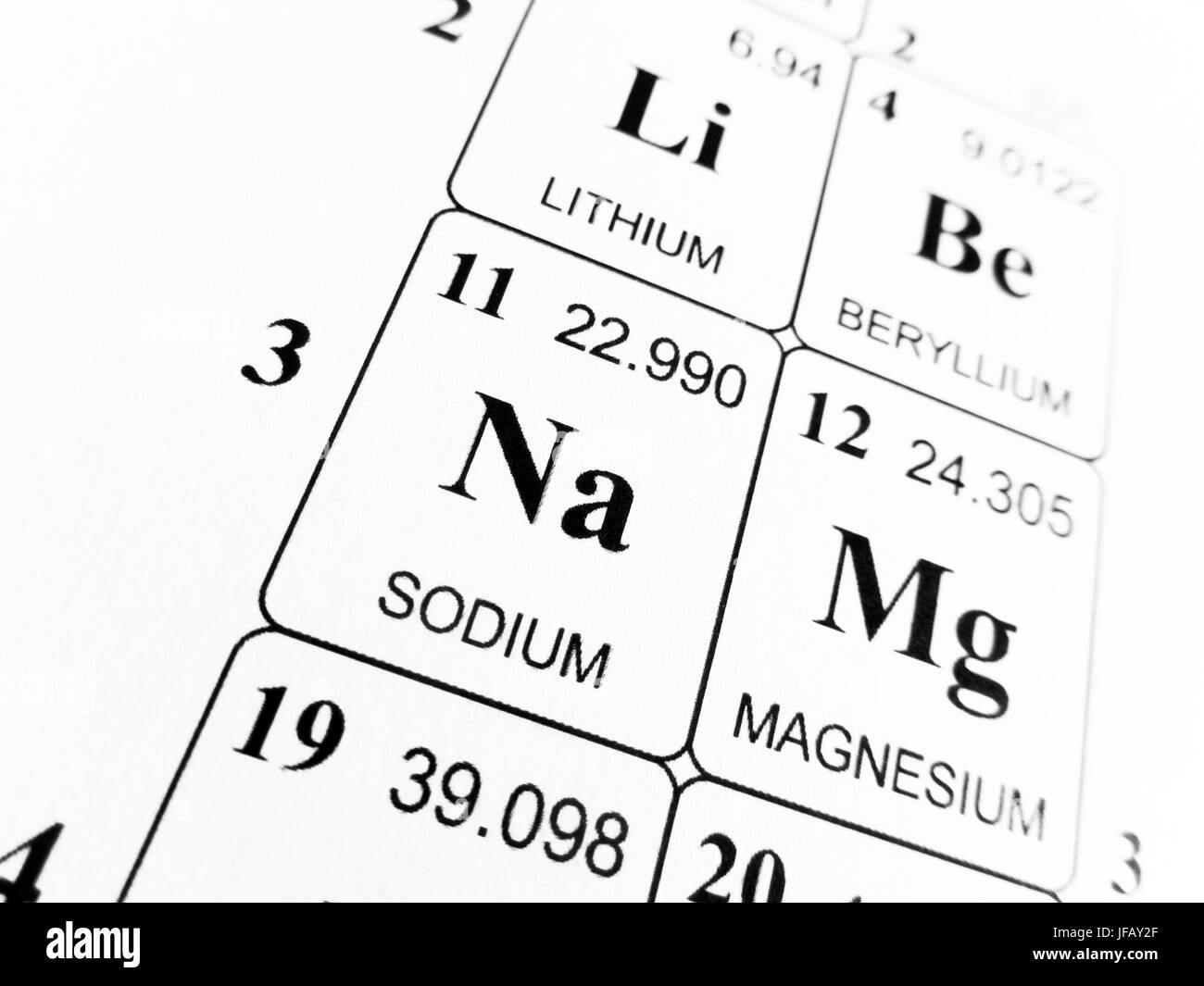
Sodium chloride
Mass number = 23
Atomic number = 11
Relative atomic mass of sodium = 23
Mass number = 35.5
Atomic number = 17
Relative atomic mass of chlorine = 35.5
Sodium chloride molecules consist of a sodium atom and a chlorine atom. The calculation is:
Relative Atomic Mass Of Sodium Chloride

Relative Atomic Mass Of Sodium Fluoride
Free download google chrome for mac. 23 + 35.5 = 58.5
So the relative formula mass of NaCl is 58.5
Finding the relative atomic mass of an element with isotopes
As explained earlier, for most elements the relative atomic mass is equal to their mass number.
Atomic Mass Of Sodium Bicarbonate
However, if you want to find the relative atomic mass of an element with various isotopes, such as chlorine, then you need to find the average atomic mass of its isotopes. You also need to know the relative abundance of the element.

The relative abundance is how much there is of each isotope compared to the total amount of the element.
Chlorine
For example, there are two isotopes of chlorine. One has a relative mass of 35 (chlorine-35) and the other has a relative mass of 37 (chlorine-37). In a sample of chlorine gas, 75% is chlorine-35 and 25% is chlorine-37. These percentages are the relative abundances of the isotopes.
To work out relative atomic mass, multiply the mass of each isotope by its relative abundance. Then add those numbers together and divide by the sum of the relative abundances.
Relative Atomic Mass Of Sodium
The calculation for working out the relative atomic mass of chlorine is:
(25%x37) + (75%x35) = 9.25 + 26.25
=35.5
Streaming video software for mac. Therefore, the relative atomic mass of chlorine is 35.5.
Summary
If you see the word ‘relative’, it means mass number.
The relative atomic mass of an element is simply its mass number, unless the element has various isotopes (like chlorine). In this case, find the average of the mass numbers of the isotopes, taking their relative abundances into account.
To work out relative formula mass, add up the mass numbers of all the elements in a compound.
