We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Begins friendship with Tolstoy, who shared Fet's distaste with the liberal critics; later introduces Tolstoy to the works of Schopenhauer. 1877 Buys a larger estate where he winters. 1878 Writes 'Death' another of his death wish poems 1881 Translates Schopenhauer into Russian. A very successful tracer in this field is O- (2- 18Ffluoroethyl)-L-tyrosine (FET) which in recent years has replaced short-lived tracers such as 11C-methyl-L-methionine in many neuro-oncological centers in Western Europe. FET can be produced with high efficiency and distributed in a satellite concept like 2- 18Ffluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose.
- Fets Luck Meaning
- Fetus In A Fetus
- What Happens In A Fet
- In A Fetus The Lungs Are Collapsed. This Makes It
- In A Fetus Where Are Lymphocytes Produced Mcq

How is FET a voltage controlled device?
the voltage applied between the gate and the source controls the drain current (id). which means you use the voltage to control the output current. therefore, fet is a voltage controlled device.
just explained because it consumes very little power to operate. it relies on the voltage differential to create a field effect necessary for its operation (hence the field effect transistor name). the amplitude of the voltage differential dictates the operating speed of the device.
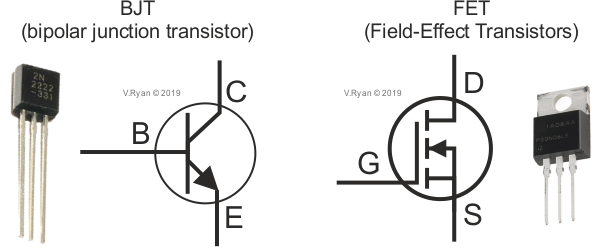
A FET is voltage controlled device by virtue of the fact that current flow between the Drain and the Source is controlled by the voltage at the Gate in reference to the Source (Vgs).
Fets Luck Meaning
a fet is controlled by a voltage at the terminal of the gate and, because of the very high grid impedance, flows in or out of the gate. compare to a bipolar transistor in the active state which is controlled by the current flowing from the base to the emitter, which allows to obtain a collector-emitter current proportional to the base-emitter current.

a fet is a voltage-controlled device because the current between the drain and the source is controlled by the voltage at the gate with reference to the source (vgs).
This contrasts with the current controlled bjt because the current flow between the collector and the emitter is controlled by the current flowing through the base.
why is a FET voltage controlled device?
The most common type of fet is a type of insulated door. since the door is isolated from the drain and the source, no current can cross it (or very little, in practice). the fet has no choice: it can not be controlled by the current, it must be controlled by the electrostatic field created by the voltage on its grid. (hence its name: field effect transistor.)
or something like that!
To be short and simple:
Fetus In A Fetus
You vary the voltage at the terminal, you get a constant current at the output. this is because the gate voltage is used to control channel resistance or pinch condition.

While a transistor is a current-controlled device because the base current is used to control the output collector current (taking into account the configuration of the common emitter).
in practical cases, the mosfet is better than the fet (the effects of ionization in the fet make it unfit for use in practical circuits). that’s why we’ve installed a layer of metal oxide on the fet to improve its applications.
For more detailed explanations, study the output response graphs of fet and compare them with those of mosfet.
jfet is a voltage-controlled device because the input signal is applied to the reverse-biased pn junction (source gate), which allows only a leakage current (in nano amps). the input bias current is negligible, the voltage having a dominant effect (very high impedance of 100 megohms). the output current flows from the source to the drain; the variation of the gate voltage controls the drain current. Instrumentation amplifiers
jfet are used to amplify thermocouple signals in the microvolt range since virtually no bias current is drawn from the sensor.
by comparing bjt, it uses a live-biased pn junction inrush current in a range from micro to milliamps, resulting in low input impedance. Here, the change of the base current controls the greatest variation of the current of the collector. therefore, bjt is a current controlled apparatus.
it can be noted that in the two amplifiers bjt jfet, the voltage signals are given as input.
Which device is a voltage controlled device?
A transistor drain is part of a field effect transistor, commonly called a FET, and the equivalent of the emitter on a standard semiconductor transistor. A FET has four basic components and corresponding terminals called the gate, the source, the body, and the drain. When a control voltage exists at the FET’s gate and body, any electrical signal waiting at the source will travel from the source to the transistor drain and out of the drain’s terminal. Thus, a transistor drain can refer to either the output component of a field effect transistor or the terminal that connects the component to other circuitry.
While field effect transistors perform functions similar to standard junction type transistors, how they perform those functions is very different. A regular transistor is made of three pieces of material carrying an alternating static charge, either positive-negative-positive, called PNP, or negative-positive-negative, called NPN. These pieces, called the collector, emitter, and base, are fused together, which essentially creates a diode with either two anodes or two cathodes.
If an electrical signal is waiting at the transistor’s collector and there is no voltage at the base, the transistor is said to be switched off and does not conduct an electrical signal. Should voltage then enter the transistor’s base, it alters the electrical charge of the base. This change in charge switches the transistor on, and the collector signal conducts through the transistor and out of its emitter for use by other electronic circuitry.
Field effect transistors operate on an entirely different principle. A FET is comprised of four pieces of material, each with a terminal, called the source, gate, drain, and body. Of these four, only the source, drain, and body carry a static charge. Either this charge will be negative in the source and drain, called an n-channel FET, or it will be positive in both, called a p-channel FET. In either case, the body of FET will carry a charge opposite to the source and drain.
These four pieces are then assembled in an order that is also different from in standard transistors. The source and drain will be fused to either end of the body. The gate is then fused to the source and drain, bridging them but not coming into direct contact with the body of the transistor. Instead, the gate is set parallel to and at a specific distance from the body.
If the FET is an n-channel type device, either no voltage or a negative voltage connected between the source and the drain will switch the FET to an off state, and it will not conduct a signal between the source and drain. With the body of the FET charged, placing a positive voltage at the gate of the FET will switch it to an on state. The charge of the gate will begin to pull electrons from the body of the FET, essentially creating a field called the conductive channel.
What Happens In A Fet
In A Fetus The Lungs Are Collapsed. This Makes It
If the voltage at the gate is strong enough, a point referred to as its threshold voltage, the conductive channel can fully form. Once the conductive channel forms fully, the voltage at the FET’s source will then be able to conduct its signal through the conductive channel to and out of the transistor drain. If the voltage at the gate is then lowered below its threshold, the field across the gate and body of the FET will instantly collapse, taking the conductive channel along with it and returning the FET to an off state.
In A Fetus Where Are Lymphocytes Produced Mcq
FETs are very sensitive to their gate threshold voltages. Using a gate voltage that is only slightly higher than required, then lowering it only slightly, will switch the FET on and off very quickly. As a result, varying the gate voltage only slightly at a very high frequency can turn the FET off and on at much faster speeds, and with much smaller voltages, than possible with a standard transistor. The speeds at which FETs can switch make them the ideal transistors for high-speed digital circuits. They find extensive use in devices such as digital integrated circuits and microprocessors, and they are the transistor of choice for use in modern computer CPUs.
